HHV-6 reactivation much more frequent than reactivation of other herpesviruses.
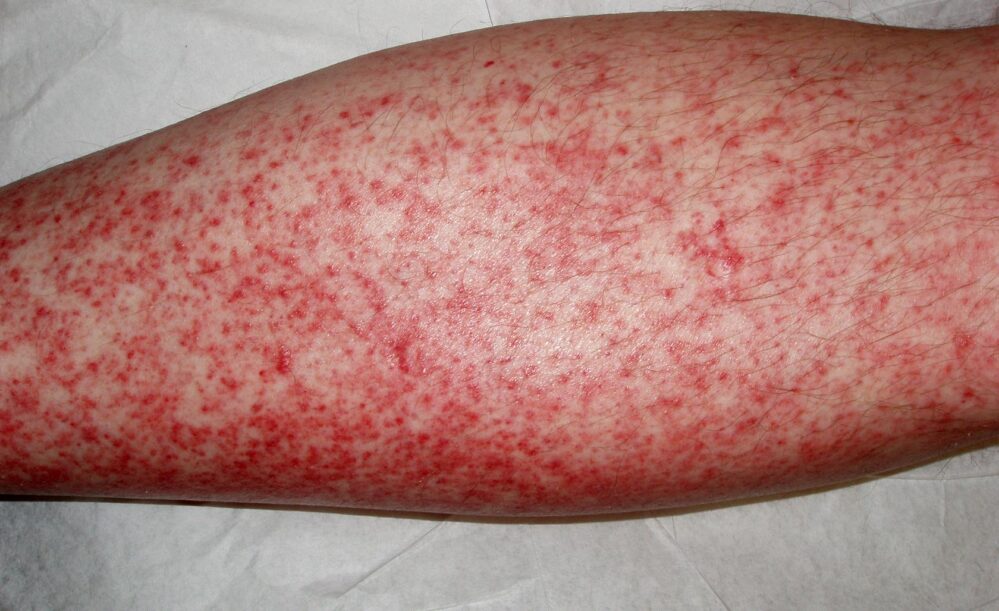
Physician-scientists at Baylor College of Medicine have published a thorough review of the evidence linking HHV-6 to DIHS/DRESS (hereafter called just DRESS). This drug-induced type IV hypersensitivity syndrome is characterized by fever, lymphadenopathy, eosinophilia, atypical lymphocytosis, skin involvement and internal organ involvement. It can be severe, even life-threatening.
The scoping review of articles identified by a PubMed/MEDLINE search included articles containing original data on at least one DRESS patient in which HHV-6 testing had been conducted. The articles included in the review involved, collectively, 748 DRESS patients who had been tested for HHV-6.
The review summarized many previous studies which have found that HHV-6 occurred much more frequently (in 62.8% of patients) than does reactivation of CMV, EBV or HHV-7, which occurred in 24.7%, 30.4% and 16.0% of patients, respectively.
The review found considerable evidence that HHV-6 reactivation is associated with significantly more long-term sequelae, longer hospital stay and other measures of severity in people with DRESS. Also, it found multiple case reports of fulminant, organ-specific HHV-6 reactivation associated with organ pathology.
Other interesting findings:
- HHV-6 reactivation occurred, on average, 21.6 days after the onset of DRESS symptoms. Although numerous cases reported HHV-6 reactivation at the onset of DRESS, none report HHV-6 reactivation prior to DRESS onset.
- Th2 cytokine thymus and activation regulation chemokine (TARC) is associated with DRESS severity and CCR4, a TARC receptor that leads to Th2 reactivation, may play a role in HHV-6 reactivation. CCR4+ monomyeloid precursors harboring HHV_6 DNA are found early in DRESS, but not in other hypersensitivity conditions. Similarly HMGB-1, a chemoattractant for CCR4+ monomyeloid precursors is also elevated in DRESS but not SJS patients (Hashizume 2013).
- Dysregulation of Th1 chemokines was also seen with HHV-6 reactivation, including increased TNF-alpha preceding reactivation.
- OX/40/CD134 is the entry receptor for HHV-6B and increased OX/40/ CD134 expression on T-cells precedes HHV-6B reactivation in DRESS, suggesting that the degree of OX40/CD134 expression on T cells may affect the likelihood and magnitude of HHV-6 reactivation.
- Several case reports, but no controlled trials thus far, suggest a value of HHV-6 antivirals such as ganciclovir and foscarnet in people with DRESS
The fact that most studies have found HHV-6 reactivation to occur some time after the onset of DRESS symptoms is not consistent with a role for HHV-6 in initiating DRESS. However, an important question to resolve is the extent to which reactivation of HHV-6 during DRESS prolongs the pathological process and contributes to organ disease and autoimmunity.
Read the full article: Zhu 2023