
Yasuko Mori, MD, PhD
Division of Clinical Virology, Center for Infectious Disease
Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine
Researchers led by Yasuko Mori of Kobe University in Japan have developed an animal model that will be useful for studying the pathogenicity of HHV-6B in conditions such as acute GVHD and idiopathic pneumonia
Although both CD46 transgenic (Reynaud 2013) and a humanized mouse model (Tanner 2013) exist for HHV-6A, a model for HHV-6B has been more challenging because HHV-6B utilizes the CD134 receptor that appears only on activated cells. The Japanese group achieved a high ratio of activated human T-cells with an intraperitoneal injection of 4-6 x 106 stimulated human cord blood mononuclear cells (CBMCs) into immunodeficient humanized mice. The CBMC transfer was followed by a “remarkable increase” in the number of activated T-cells expressing CD134, creating ideal conditions for HHV-6B infection.
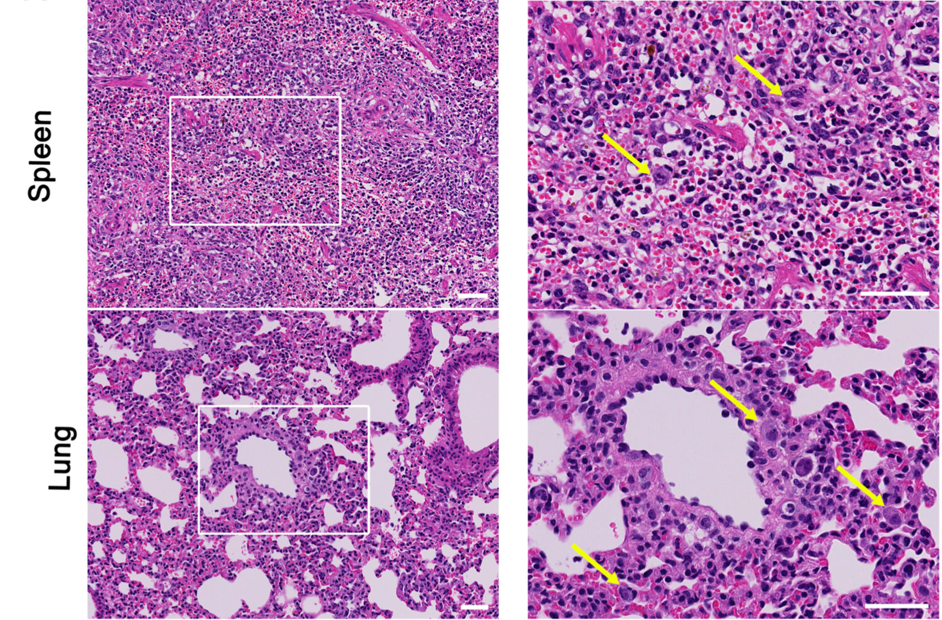
Representative histology and immunostaining of infected mice. Left pane: low power view showing infiltrations and of atypical large cells. Right panel: high power view showing infected giant cells (arrows). Source: Journal of Virology, December 2019
The clinical result in the mice was a condition similar to acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) with HHV-6B replication in all main organs, but especially high in the spleen and lungs. The investigators also observed an increase in inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in HHV-6B infected mice similar to the profile found in children with primary HHV-6B infection and to in vitro infection.
The authors propose that the relationship between HHV-6B and GVHD may be recursive; HHV-6B increases the risk of GVHD, which in turn may increase T-cell-production and expression of CD134. Their study also confirmed a “tight correlation” between the expression of CD134 and HHV-6B reactivation/replication after allogenic HSCT.
There were relatively high secretions of IL-6, IL-8, CCL2 and CCL8 in the early phase of infection. HHV-6B showed significant organ-tropism to the spleen and the lungs (~10,000 copies/ng total DNA 8 days post-infection). The observation of high levels of the virus in lung tissues supports previous studies reporting a role for HHV-6B in various lung pathologies (Seo 2015; Hill 2019; Zhou 2019).
An HHV-6/7 homolog, murine roseolovirus (previously known as murine thymic virus), has many similarities to HHV-6B and has been shown to cause T cell depletion (Patel 2017) as well as increased acute GVHD and lung fibrosis in a murine bone marrow transplant model (Zhou 2019).
The authors plan to use their HHV-6B model to further elucidate viral pathogeneses and to evaluate HHV-6B specific antivirals.
Read the full-text: Wang 2019

